Be skeptical when you hear about the return to glory of the American city — that idealized vision of rising skyscrapers and bustling, dense downtowns. Contrary to perception, the nation is continuing to become more suburban, and at an accelerating pace. The prevailing pattern is growing out, not up, although with notable exceptions.
Rural areas are lagging metropolitan areas in numerous measures, but within metro areas the suburbs are growing faster in both population and jobs.
On the other hand, as anyone who has tried to rent an apartment or buy a condo in a big city knows, housing prices are climbing faster in urban neighborhoods than in the suburbs. And urban neighborhoods are younger and richer than they used to be, with more educated residents and fewer school-age children. Higher-wage jobs are increasingly in city centers, with urban retail catering to these well-paid workers and residents.
This combination of faster population growth in outlying areas and bigger price increases in cities points to limited housing supply as a curb on urban growth, pushing people out to the suburbs. It’s a reminder that where people live reflects not only what they want — but also what’s available and what it costs.
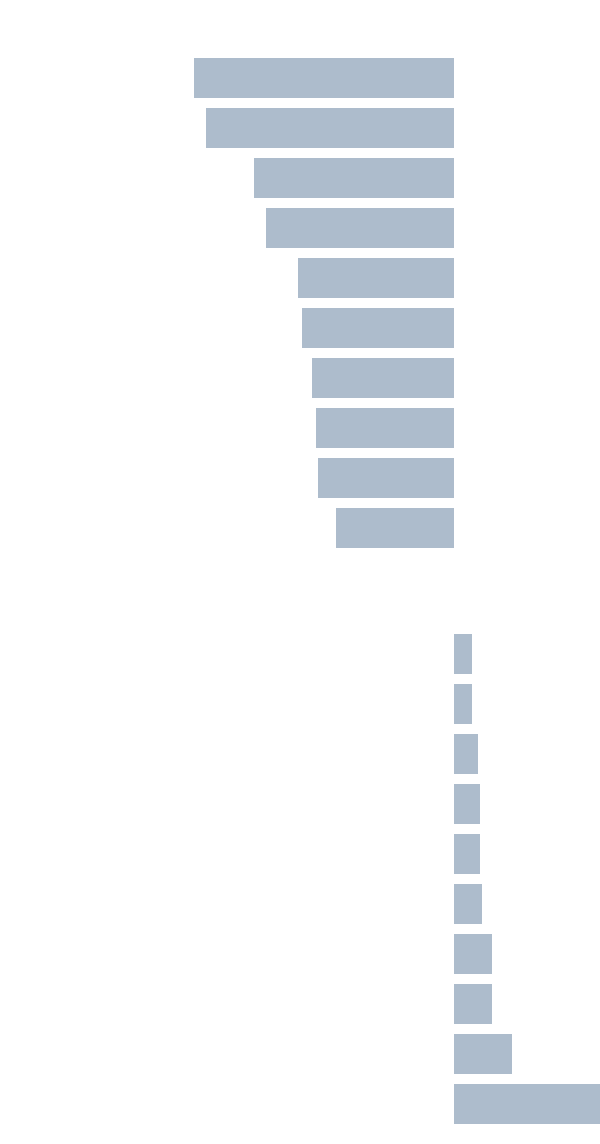
Continue reading the main storyHowever, these broad national trends hide divergent local ones. A few large metro areas did, in fact, become more urban between 2010 and 2016. Of the 51 metro areas with more than one million people, average neighborhood density rose in 10 and fell in 41, according to census population data and U.S. Postal Service counts of occupied housing units. That is, four-fifths of large metro areas have become more suburban since 2010, while only one-fifth have become more urban.
Metro Areas Heading in Opposite Directions
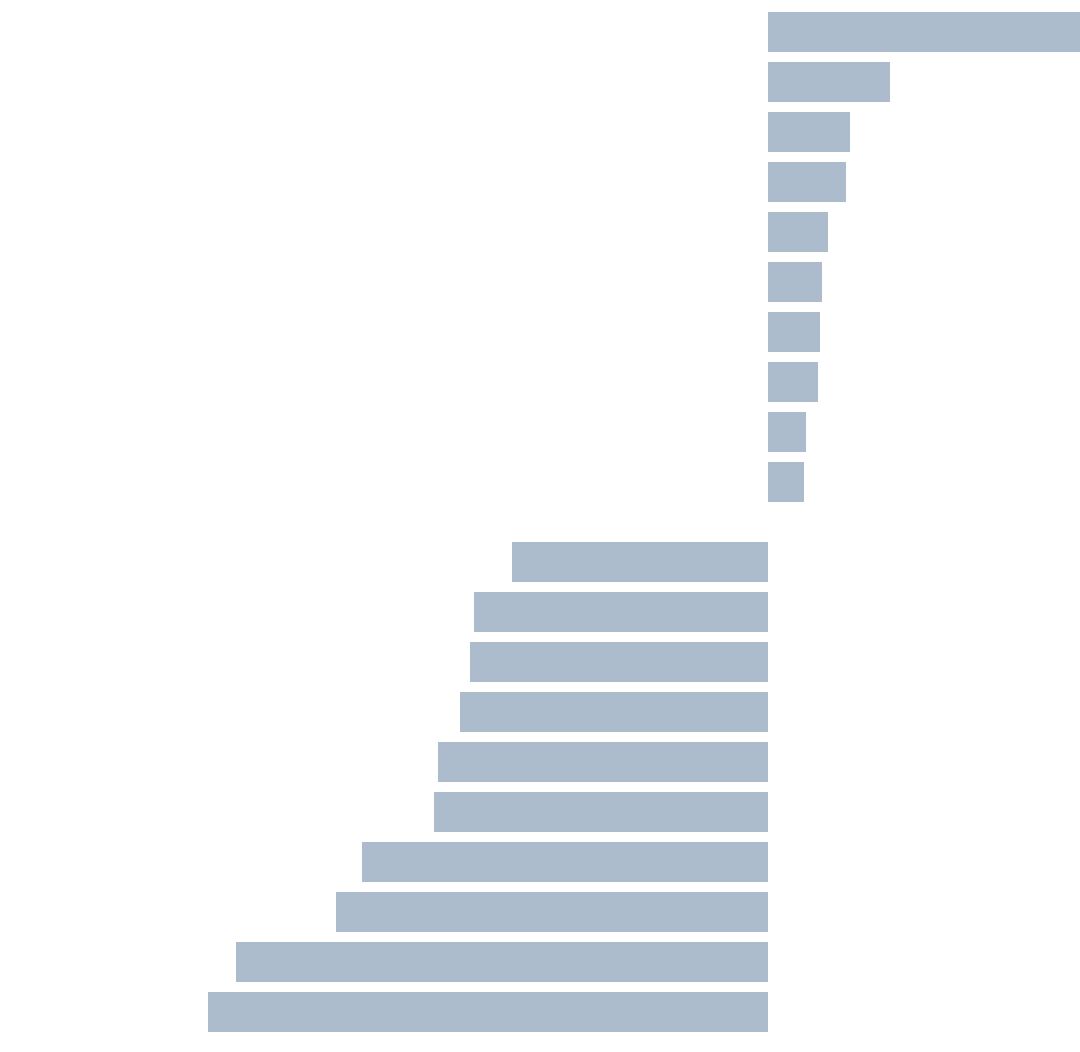
Seattle urbanized the most: Faster growth in the city’s neighborhoods meant that average neighborhood density was 3 percent higher in 2016 than in 2010. Among the sprawling majority, San Antonio and Austin spread out the most: In both cities, average neighborhood density fell by 5 percent between 2010 and 2016. All of the metro areas where density fell the most were in the Sun Belt, including Las Vegas, Houston, Dallas and Orlando. These sprawling metro areas are also showing faster overall growth than the urbanizing metro areas.
There’s a clear pattern in which metro areas are becoming more urban: Dense metros are getting denser. Meanwhile, sprawling metro areas are spreading out further. It’s another example of a polarized America, of places becoming more unlike each other: not only with respect to income inequality and politics, but also with growth patterns.
The Sprawling Majority
Between 2010 and 2016, most of America’s largest metro areas became more suburban.

All of the largest East Coast and Midwest metro areas became more dense, including New York, Washington, Boston, Philadelphia and Chicago (though less so than Seattle). These places, five of the seven densest, were already relatively tightly packed to begin with. The other two densest metro areas, San Francisco and Los Angeles, suburbanized only slightly.
By contrast, none of the places where sprawl increased most between 2010 and 2016 — Austin, San Antonio, Houston and Oklahoma City — had been especially urban even in 2010.
The metro areas that are becoming more dense include two, New York and Washington, that are home to the media outlets where much of the writing about cities appears. Furthermore, metro areas that are urbanizing have more than their fair share of urban planners, including Seattle, Minneapolis, Washington and Boston. Those who write about, advocate for and choose to live in cities really do see more urbanization around them. But their cities are the exceptions. Most large metro areas, including the fastest-growing ones, as well as America over all, are increasingly suburban.
Continue reading the main story